A–Algorithm

An algorithm is an effective method that can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time.
B–Bit
01011101101010101100101010
10101010101010000001101010
11010001010010101101010011
10101010101010101001000011
10101101110101010000010101
10101010010101010101010110
The bit is a basic unit of information used in computing and digital communications.
C–Code

Code is a system of rules to convert information.
D–Debugging

Debugging is the process of finding and resolving of defects or problem within the program that prevent correct operation of computer software or a system.
E–Error

An error is an action which is inaccurate or incorrect.
F–Function

An operator performing certain data processing operations and returning the result to the program.
G–Glitch

A glitch is a short-lived fault in a system, such as a transient fault that corrects itself, making it difficult to troubleshoot.
H–HTML

Hypertext Markup Language is the standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications.
I–IOS

iOS is a mobile operating system created and developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its hardware.
J–Java

Java is a general-purpose computer programming language.
K–Knowbot

It a kind of bot that collects information by automatically gathering certain specified information from web sites.
L–Library

is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs.
M–MIME

Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions- A protocol that defines the way that messages are transmitted over the Internet.
N–Network

Is a digital telecommunications network which allows nodes to share resources.
O–Overload

The possibility of using subprograms of the same name: procedures or functions in programming languages.
P–PHP

is a server-side scripting language designed primarily for web development but also used as a general-purpose programming language.
Q–QR code
Quick Response Code is the trademark for a type of matrix barcode (or two-dimensional barcode).
R–RGB
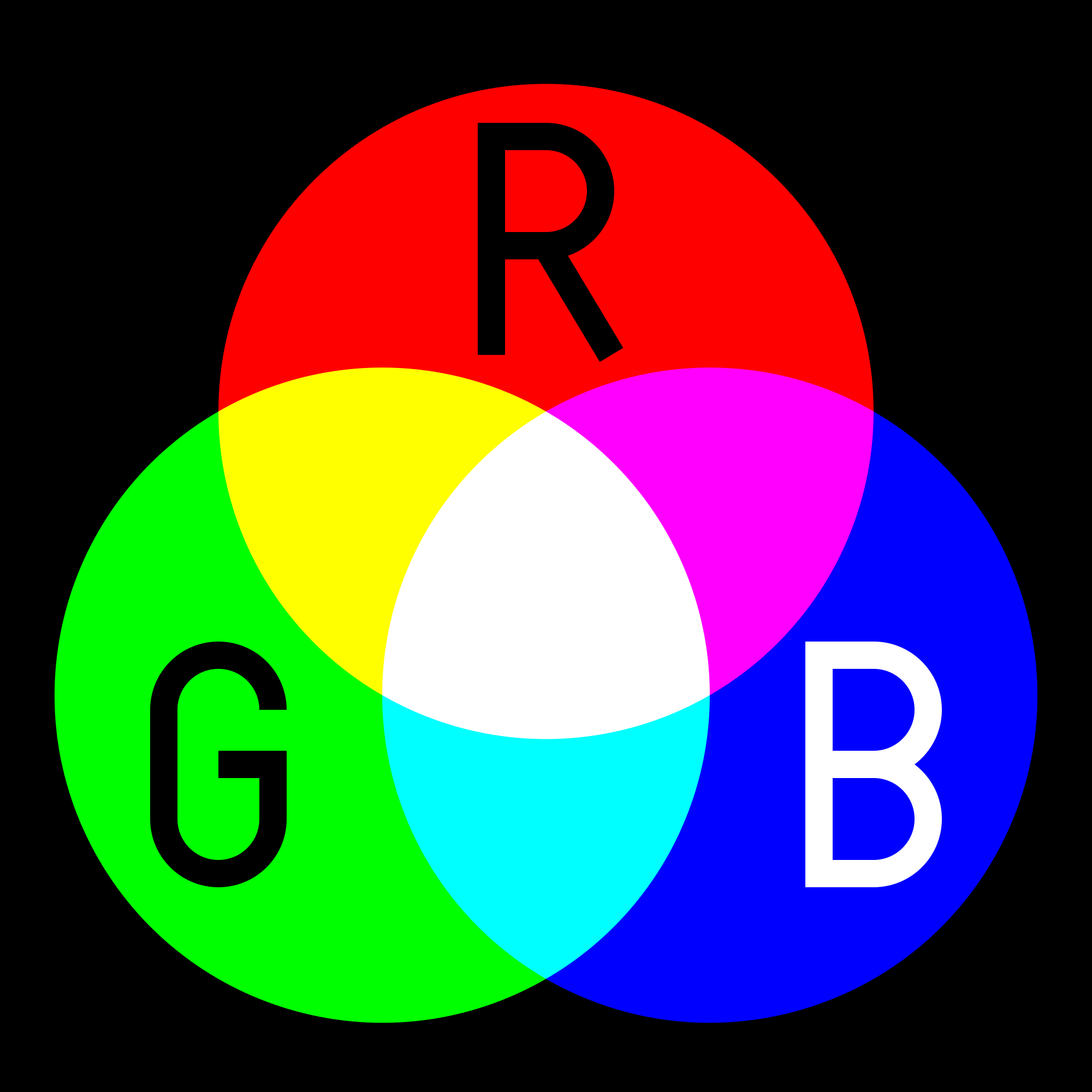
is an additive color model in which red, green and blue light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors.
S–script

programs written for a special run-time environment that automate the execution of tasks.
T–Tag
element of hypertext markup language. The text between the start and end tag is displayed and placed according to the properties specified in the start tag.
U–Unix

element of hypertext markup language. family of portable, multitasking and multi-user operating systems.
V–Visual basic
a programming language, and an integrated software development environment developed by Microsoft.
W–Windows OS
a family of proprietary operating systems from Microsoft, focused on the use of the graphical interface for management .
X–XML

The markup language for web pages, which is the successor of HTML.
Y–Yahoo

This is a search engine
Z–ZIP file
a popular format for archiving files and data compression without loss.
Published: Nov 5, 2017
Latest Revision: Nov 5, 2017
Ourboox Unique Identifier: OB-380826
Copyright © 2017